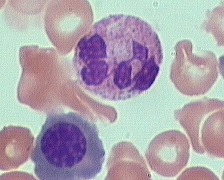
LEFT SHIFT
Istilah " left shift " bermakna populasi beberapa sel-sel
"beralih" ke arah prekursor belum matang (bermaksud bahawa terdapat
lebih prekursor belum matang daripada yang biasa anda lihat). Jika anda lihat
siri neutrophil, sebagai contoh. Dalam darah normal, hampir kesemua neutrofil
adalah matang (bersegmen). Dalam " left shift ", anda dapat lihat
neutrofil yang matang tetapi juga neutrofil yang tidak matang (band,
metamyelocytes, myelocytes, dll). Lihat gambar " left shift ", di
atas: kebanyakan sel-sel tidak matang.
Rajah : Diagram "Left Shift"
Istilah " left shift "
adalah merujuk kepada siri neutrophil. Ianya mula digunakan dahulu apabila pengiraan
sel-sel dilakukan secara manual. Kedudukan sel-sel yang paling matang (neutrophil
bersegmen) diletakkan untuk butang yang paling kanan, sel-sel kurang matang (myeloblasts)
telah diletakkan kepada butang yang paling kiri, dan peringkat sel-sel yang lain
terletak diantaranya. Dalam PBF darah yang normal, hampir semua neutrofil terletak
di bawah butang paling kanan dalam pengiraan, tetapi kadang-kadang terdapat juga
precursor yang awal (contohnya, myelocytes, metamyelocytes, atau
promyelocytes). Dalam keadaan ini, sel-sel telah "shifted" ke arah
kiri.
Bagi kebanyakan kes, apabila terdapat
situasi " left shift ", selalunya pesakit mempunyai jangkitan bakteria.
Kadang-kadang " left shift " juga berlaku apabila terdapat keradangan atau
nekrosis.
Berhati-hati, jika anda melihat “nucleated
RBC” bersama keadaan " left shift ". Ini dipanggil tindak balas
leukoerythroblastotic, ia mungkin menunjukkan masalah yang lebih serius.
Kadang-kadang, satu tindak balas leukoerythroblastotic adalah psikologic.
Jika hemoglobin adalah sangat rendah (untuk apa jua sebab - kekurangan zat besi
yang teruk, kehilangan darah secara besar-besaran), sum-sum tulang akan cuba
sedaya upaya untuk menghasilkan sel-sel merah baru dan menghantar mereka keluar
ke dalam salur darah secepat mungkin. Keperluan mendesak ini kadang-kadang
menyebabkan beberapa prekursor sel darah merah (nucleated RBC) terlepas
dari sum-sum tulang. Dan ia juga mula membiarkan prekursor neutrophil
(metamyelocytes, myelocytes, promyelocytes) dikeluarkan. Ini adalah tindak
balas yang normal kepada kes anemia yang
teruk.
Tindak balas
leukoerythroblastotic juga berlaku jika sumsum penuh dengan sesuatu selain tisu
hematopoietik - sebagai contoh, carcinoma, atau leukemia - maka sel-sel
hematopoietik tidak akan mempunyai ruang yang cukup untuk matang secara
sempurna. Sel-sel ini akan keluar meninggalkan sum-sum sebelum mereka matang,
dan anda akan melihat kedua-dua sel “nucleated RBC” dan prekursor neutrophil
dalam darah. Ini bukanlah sesuatu yang baik..
Figure 1: Haematopoiesis cell development pathways.